Imagine booking a flight, applying for travel insurance, and paying for it—all without leaving the airline’s app. Or splitting the cost of groceries into installments at checkout, seamlessly. These frictionless experiences are no longer a luxury; they are the new normal, enabled by the transformative power of embedded finance.
Embedded finance is reshaping the financial services landscape. By integrating payment, lending, insurance, and banking services directly into non-financial platforms, businesses are creating smoother customer journeys and unlocking significant growth opportunities. This evolution is driven by fintech companies and traditional banks collaborating to embed financial solutions into everyday platforms.
Embedded finance is rapidly transforming the financial landscape. 56% of businesses already offer at least one form of embedded finance, while 55% of non-financial businesses plan to introduce these services within the next two years. This trend signals not only widespread adoption but also a shift in how financial services are delivered.
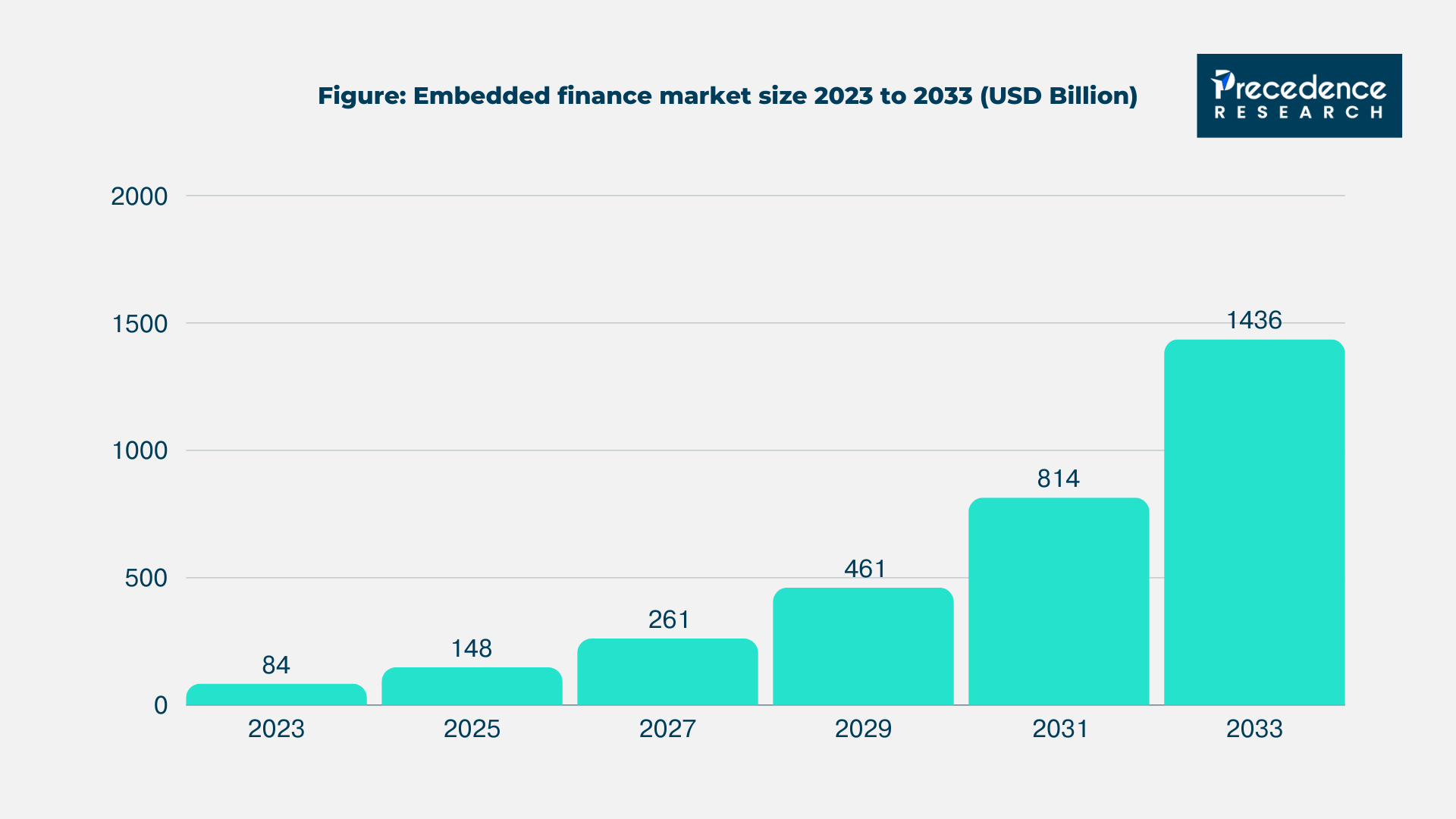
The U.S. market is a prime example of this growth. Transaction volumes in the embedded finance sector reached $2.6 trillion in 2021 and are projected to surpass $7 trillion by 2026 (Bain & Company). Globally, the embedded finance market is estimated at $84.12 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow at a CAGR of 32.81% to reach $1.43 trillion by 2033 (Precedence Research).
Major players like Unit and Walnut are driving innovation by enabling businesses to embed financial services like banking, lending, and insurance into their platforms. Additionally, the rise of digital wallets, BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later) services, and mobile payments have fueled this market’s expansion, as evidenced by 45% of Gen Z and Millennials using BNPL in the past year.
The impact of embedded finance goes beyond convenience; it creates significant economic opportunities:
Embedded finance also enhances security and efficiency, with AI-powered systems reducing fraud by up to 50%. Furthermore, 86% of U.S. mobile wallet users have purchased through retailer-embedded apps (Marqeta), demonstrating the importance of integration in customer engagement strategies.
This momentum underlines the importance of embedded finance for businesses seeking to deliver seamless user experiences, improve financial inclusion, and unlock new revenue streams.
Key Insight: Embedded finance isn’t just a convenience—it’s a redefinition of how consumers interact with financial services and how businesses operate. But, the challenges of scaling these solutions efficiently can be daunting.
At its core, embedded finance integrates financial services like payments, lending, insurance, or banking into non-financial platforms through APIs. This is a transformative approach, turning traditionally standalone financial functions into seamless parts of user experiences.
Here’s a breakdown of the main types, including notable examples of startups in these different categories:
Consumers love simplicity. Embedded finance removes the friction of switching between apps, offering everything in one place. 85% of consumers say they prefer platforms that simplify their financial interactions (Source: Finextra). Moreover, as deigital-native generations become the dominant consumers group, the demand for integrated frictionless financial services has surged.
This trend is evident across various sectors, including retail, traveltech, healthcare, mobility…, as businesses directly leverage tech to offer services like payments, lending and insurance within their ecosystems.
For instance, companies like Ford and Jaguar Land Rover have begun integrating insurance policies directly within vehicle purchases or leases, enhancing customer satisfaction an streamling the budying process.
Businesses are integrating embedded finance to stand out in competitive markets, creating growing demand for your solutions. Non-financial companies can monetize financial services, creating new revenue streams. For example, embedding lending or BNPL services boosts customer retention and increases average order value.
Additionally, business can also gain valuable insights into consumer behavior through embedded finance, allowing them to refine their products and services further.
According to research by Ayden and BCG (2024), SaaS platforms that embed financial products are poised to grow their revenues by 3-4x. The report also highlights a transformative $185 billion market opportunity for SaaS platforms—a remarkable 25% growth since 2022. BCG’s analysis attributes this market expansion to a favorable interest rate environment, driving higher bank revenues from accounts and a broader increase in overall banking revenue pools.
APIs and fintech platforms like Plaid, Stripe, and Unit make embedding finance easier than ever.
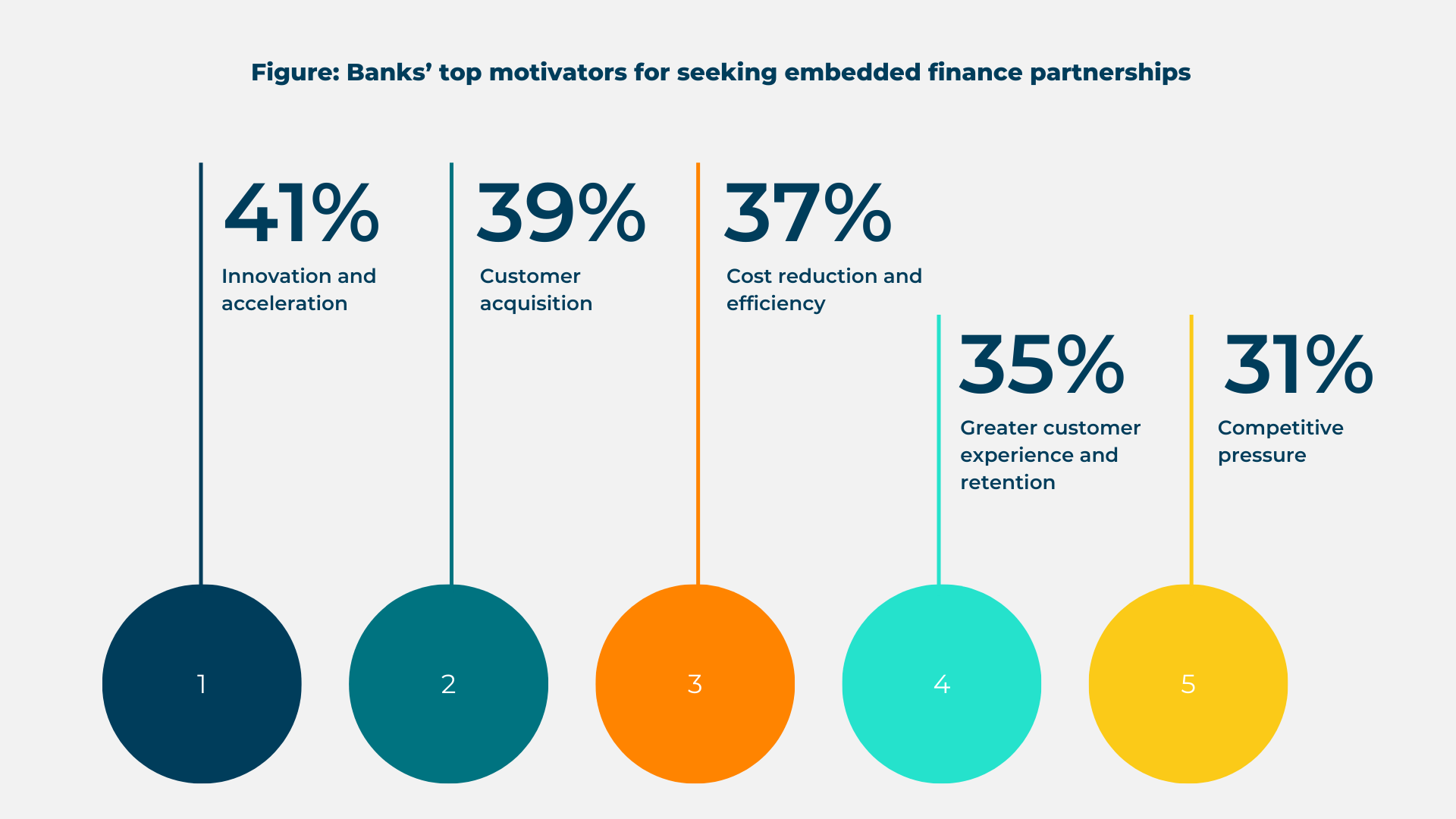
For instance, these are banks’ top motivators for seeking embedded finance partnerships (Alloy, 2024).
For fintech companies, the surge in embedded finance represents a significant growth opportunity. With their technological expertise, they are uniquely positioned to partner with non-financial brands, providing seamless financial services and broadening their market presence.
Stat to Highlight: The global embedded finance market is expected to reach $138 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 20.5% (Source: Juniper Research).

Despite its rapid growth and adoption, embedded finance brings unique challenges that fintechs must navigate to thrive. These challenges span operational, technical, and regulatory domains, often requiring strategic solutions to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
The embedded finance lifecycle involves multiple intricate processes, including onboarding users, payment processing, reconciliation, and fraud detection. A significant pain point for 66% of European firms is payment reconciliation, which is often hindered by fragmented or outdated systems. This issue is further compounded in international operations, where varying infrastructure, currencies, and compliance requirements create additional hurdles (Research and Markets).
Key Issues:
Operating across multiple jurisdictions is a double-edged sword for embedded fintechs. While it opens new markets, it also requires compliance with a myriad of local, regional, and global regulations such as PSD2 in Europe or GDPR for data privacy.
Key Statistics:
Key Issues:
Embedded fintechs often experience rapid growth, particularly during seasonal peaks or following successful partnerships. However, scaling operational infrastructure to handle surges in transactions, customer support queries, and fraud monitoring presents significant challenges.
Key Issues:

Technology underpins embedded finance, but gaps in system integration can hinder its potential. 64% of firms identify interoperability as a major challenge, highlighting difficulties in achieving seamless communication between payment gateways, vendor platforms, and internal systems.
Key Issues:
Example: A healthcare app offering embedded insurance struggled to sync policy data across its payment and claims platforms, delaying reimbursements by weeks.
To overcome these challenges, embedded fintechs are increasingly turning to outsourcing and partnerships to focus on their core offerings while delegating operational complexities to experts.
Key benefits of outsourcing:
Outsourcing providers can adapt to seasonal or unexpected spikes in transaction volumes, ensuring seamless operations during high-demand periods.
Dedicated compliance teams stay updated on evolving regulations, minimizing the risks of non-compliance.
24/7 support in multiple languages enhances global customer satisfaction and retention.
By outsourcing non-core activities like fraud detection, firms can allocate resources to innovation.
Embedded finance is your arena, and the opportunities are immense. But scaling to meet the growing demands of businesses and consumers requires more than just innovation—it takes smart partnerships.
By outsourcing non-core operations like customer support, compliance, and operational scaling, you can focus on what matters most: building the best financial tools for your clients.
Let’s partner to help you power seamless experiences for your customers—and grow your business faster.